IoT technology Security threads and Modeling Java-based IoT network attacks.
Abstract The purpose of this is to demonstrate the security gaps in the Object Network using the Distributed Denial of Service Asset technique. It summarizes the structure of DPA, general information as well as forms of attacks that threaten them as they become more and more popular. Rapidly developed human need for immediate availability of […]

Abstract
The purpose of this is to demonstrate the security gaps in the Object Network using the Distributed Denial of Service Asset technique. It summarizes the structure of DPA, general information as well as forms of attacks that threaten them as they become more and more popular. Rapidly developed human need for immediate availability of real-time data and information has led the world of technology to the creation of a new form of networking that is implemented with the participation of interconnected devices, which are able to collect and send information in real time . The morphology and structure of these networks is very heterogeneous both for the entities and for the technologies involved. The general form of these networks is divided into two major categories. Closed / private IoT networks such as local / private networks, e.g. home, corporate, and open networks as defined by public broadband and coverage networks. The structure of these networks varies considerably, yet they have the same logic and purpose of existence. Both form networks consist of devices that interact in real time by sending and receiving information. The potential benefits of IoT can be described as unlimited as well as its applications that can radically change the way we work and live.
The chapters below will initially analyze the general structure of the IoT morphology, and then make further reference to the gaps and security problems faced by these networks. The work includes an experimental part that implements a Distributed Denial of Service Attack in a virtual closed loop network environment.
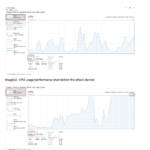
The experimental part focuses on demonstrating the vulnerability of these networks to the particular form of attack that can be implemented in various ways and methods. Entities launching attacks are implemented using an object-oriented programming language. Client-implemented client entities have the ability to send HTTPS network traffic to the server, which is also implemented using code. The attacking client entities launch a simultaneous attack on the server in order to cause the server to refuse to provide services to customers who serve legitimate customers.